0. DEFINITIONS
Important notes:
The PDF document hosted on this page is the authoritative version of the Policy Manual. The web version is provided to make it easier for readers to quickly browse the different sections of the Manual.
In the event of a conflict between the web version and the pdf version of the Manual, the pdf version shall control.
This document and/or information was originally written in Spanish, the official language of Uruguay, the country where LACNIC is legally incorporated and whose laws and regulations LACNIC must meet. Likewise, unofficial information and/or documents are also written in Spanish, as this is the language in which most of LACNIC's collaborators and officers work and communicate. We do our best to ensure that our translations are reliable and serve as a guide for our non-Spanish-speaking members. However, discrepancies may exist between the translations and the original document and/or information written in Spanish. In this case, the original text written in Spanish will always prevail.
The following terms and their definitions are of great importance for the correct comprehension of the objectives, context and policies described herein.
IP address allocation follows a hierarchical scheme. Responsibility for the administration of number resources is distributed globally in accordance with the hierarchical structure shown below.
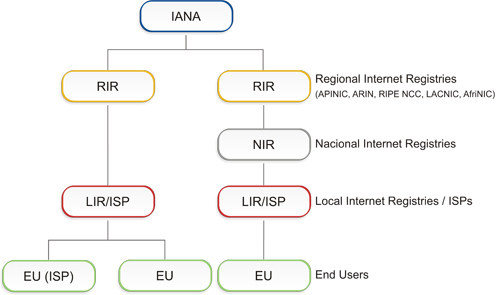
0.1.IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority)
IANA is responsible for allocating part of the global IP address space and autonomous system numbers to Regional Registries according to established needs.
0.2.Internet Registry (IR)
An Internet Registry (IR) is an organization responsible for allocating IP address space to its members or customers and for registering those allocations. IRs are classified according to their main function and geographic area of coverage as indicated in the hierarchical structure defined in the figure above.
0.3.Regional Internet Registry (RIR)
Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) are established and authorized by their respective regional communities, and recognized by the IANA to serve and represent large geographical regions. The primary role of RIRs is to manage and allocate Internet resources within their own respective regions.
0.4.National Internet Registry (NIR)
A National Internet Registry (NIR) primarily allocates Internet resources to its members or constituents, which are generally LIRs.
0.5.Local Internet Registry (LIR)
A Local Internet Registry (LIR) is an IR that primarily assigns Internet resources to the users of the network services it provides. LIRs are generally ISPs, whose customers are primarily end users and possibly other ISPs.
0.6.Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Internet Service Providers mainly assign IP address space to end users of the network services they provide. Their clients may be other ISPs. ISPs do not have geographical restrictions as do NIRs.
0.7.End Site or End User (EU)
An end site is defined as an end user (subscriber) that has a legal or commercial relationship (the same or associated entities) with an Internet service provider which involves:
- the service provider assigning address space to the end user
- the service provider offering transit services for the end user towards other sites
- the service provider transporting the end user’s traffic
- the service provider announcing an aggregated route prefix which contains the address space assigned by LACNIC to the end user
0.8.Allocate
To allocate means to distribute address space to IRs for the purpose of subsequent distribution by them.
0.9.Assign
To assign means to delegate address space to an end user, to be exclusively used within the infrastructure operated by said end user, as well as for interconnection purposes.
The assigned address space must only be used by the original recipient of the assignment, as well as for third-party devices provided they are operating within said infrastructure.
Therefore, sub-assignments to third parties outside said infrastructure (for example, the use of end-user assignments for ISPs or similar clients) and providing addresses to third parties in data centers (and others) are not allowed.
0.10.The Internet Registry System
The Internet registry system has been established with the aim of enforcing the objectives of exclusivity, preservation, routability and information. This system consists of hierarchically organized Internet registries (IRs). Internet number resources (addresses, ASNs, others) are typically assigned to end users by ISPs or NIRs.
These resources are previously allocated to NIRs and ISPs by the Regional Internet Registries.
Under this system, end users are organizations that operate networks that use the resources. Just as LACNIC, NIRs maintain resources for making assignments to end users or allocations to Internet Service Providers. Assigned resources are used to operate networks, whereas allocated resources are kept by Internet Registries for their future assignment to end users.
Note that the resources allocated or assigned by LACNIC or by the NIRs are to be used exclusively by their recipient or by third parties authorized by the recipient, provided that the policies currently in force allow such use. We recommend that such authorizations can be verified using RPKI.
0.11.Multihomed
A site is considered to be multihomed if it receives full-time connectivity from more than one Internet service provider and has one or more routing prefixes announced by at least two of its upstream providers. Independent providers refer to the fact that one does not reach the Internet through the other.